Processing Data¶
Processing Network Page¶
Files Network Within Data Type¶
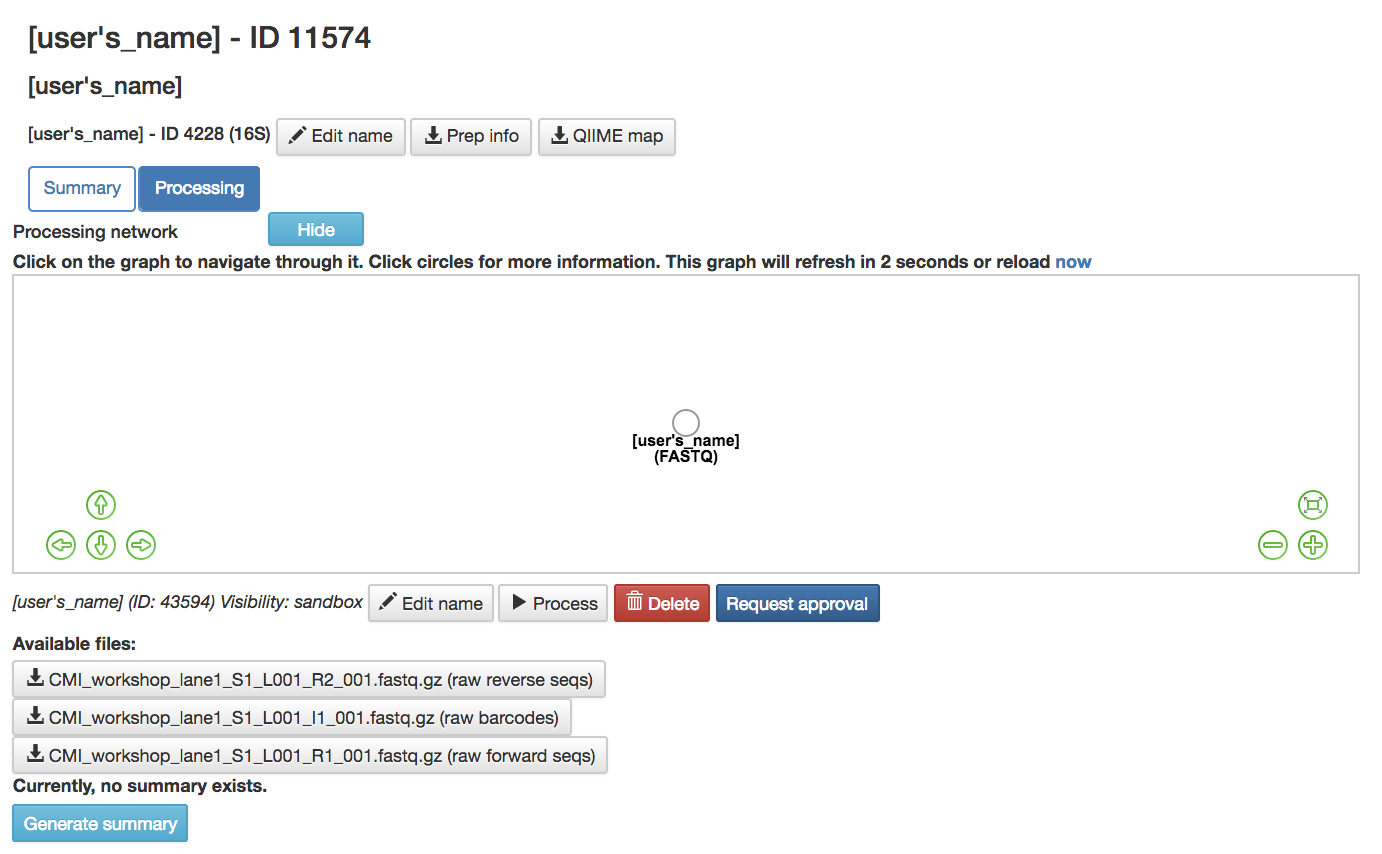
(FASTQ) or other data type artifact: Represents the data from the study
Hide: Hides the processing network
Show: Shows the processing network
Run: Runs the command that is in the processing workflow window
Click on artifact circle: Brings up more options
Edit: Rename the artifact
Process: Brings you to processing network page so you can process the data
Choose Command dropdown menu: Will show you the commands that can be given to the chosen artifact
Delete: Delete the artifact/data from the files network
Available Files: FASTQ files that have been uploaded to this study can be downloaded here
Generate Summary: Creates a summary for the data attached to the artifact chosen
Show processing information: Shows the processing information of the artifact chosen
Request Approval: Sends the artifact to a Qiita admin to be reviewed for approval to become a public study
Note that a study must be successfully processed to be approved my a Qiita admin
Note that a study must be approved by a Qiita admin prior to being sent to EBI for submission
The commands run on this page use the QIIME2 [1] bioinformatics platform.
Processing Recommendations¶
Looking for information about processing data? Please see the document here:
Converting Data to BIOM Tables¶
BIOM¶
No manipulation is necessary
FASTQ, SFF, FNA/QUAL, or FASTA/QUAL Files¶
Per-sample vs Multiplexed FASTQ Demultiplexing
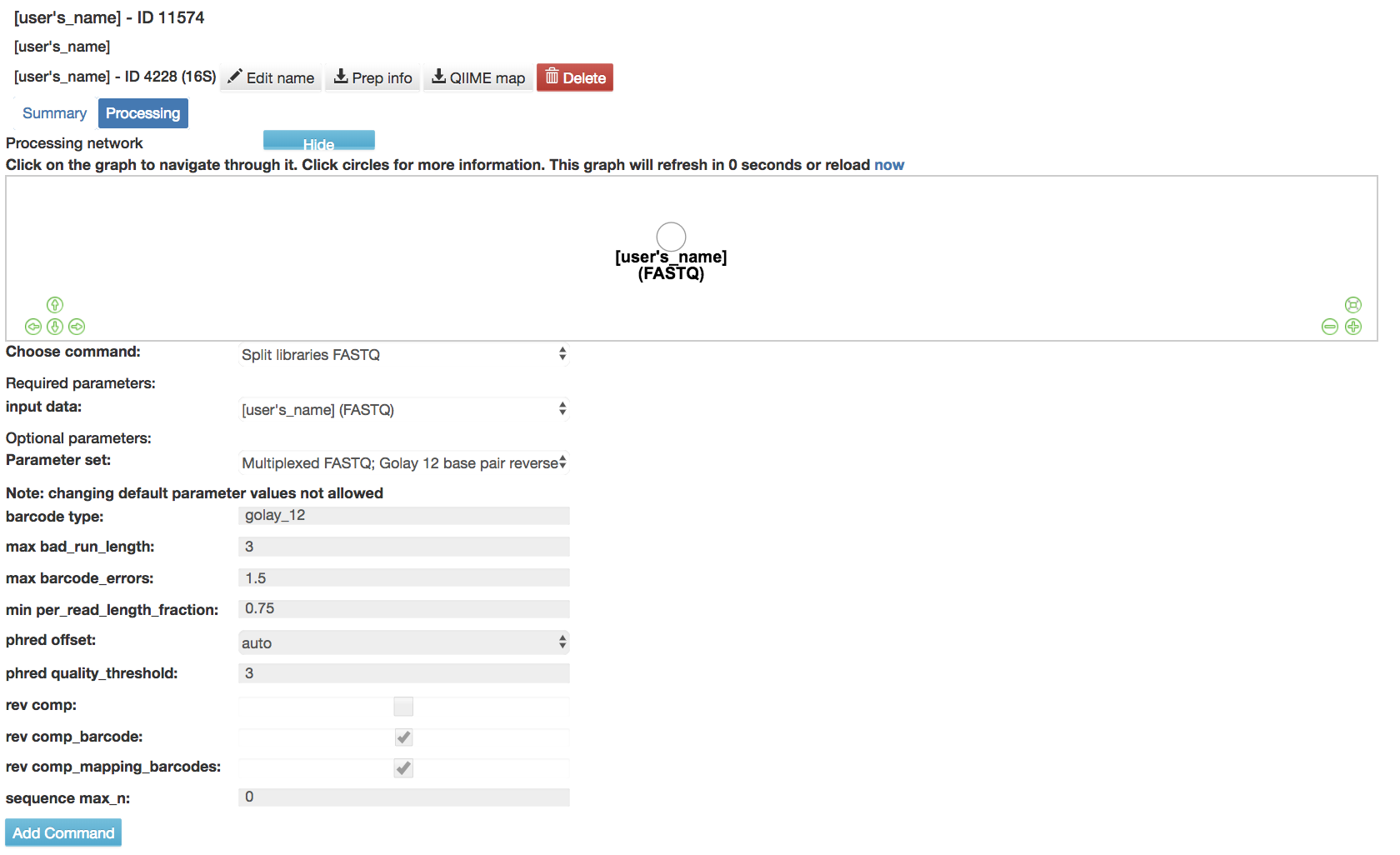
Split libraries FASTQ: Converts the raw FASTQ data into the file format used by Qiita for further analysis
Input data (required): Data being split
Parameter Set (required): Chooses the parameters for how to split the libraries
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 5 base pair barcodes: Uses first 5 base pairs to identifies samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 5 base pair barcodes with Phred quality threshold: 0 [2] : Uses first 5 base pairs to identifies samples from FASTQ from multiple samples, only use samples with Phred quality score above 0
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 5 base pair reverse complement mapping file barcodes: Uses the complementary base pairs to the last 5 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 6 base pair barcodes: Uses first 6 base pairs to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 6 base pair reverse complement mapping file barcodes: Uses the complementary base pairs to the last 6 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 8 base pair barcodes: Uses first 8 base pairs to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 8 base pair barcodes with Phred offset: 33 [2] : Uses first 8 base pairs to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples, uses Phred offset: 33 for measuring quality
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 8 base pair reverse complement mapping file barcodes: Uses the complementary base pairs to the last 8 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 11 base pair barcodes: Uses first 11 base pairs to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 11 base pair reverse complement barcodes: Uses the complementary base pairs to the last 11 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 12 base pair barcodes: Uses first 12 base pairs to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; generic 12 base pair reverse complement barcodes: Uses the complementary base pairs to the last 12 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair barcodes [3] , [4] : Error correcting for the first 12 base pairs from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair barcodes with Phred offset: 33 [4] , [2] , [3] : Error correcting for the first 12 base pairs from FASTQ from multiple samples, uses Phred offset: 33 for measuring quality
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair barcodes with Phred offset: 64 [4] , [2] , [3] : Error correcting for the first 12 base pairs from FASTQ from multiple samples, uses Phred offset: 64 for measuring quality
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair reverse complement barcodes [4] , [3] : Error correcting for the complementary base pairs to the last 12 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair reverse complement barcodes with Phred offset: 33 [4] , [2] , [3] : Error correcting for the complementary base pairs to the last 12 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples, uses Phred offset: 33 for measuring quality
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair reverse complement barcodes with Phred offset: 64 [4] , [2] , [3] : Error correcting for the complementary base pairs to the last 12 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples, uses Phred offset: 64 for measuring quality
Multiplexed FASTQ; Golay 12 base pair reverse complement mapping file barcodes with reverse complement barcodes (UCSD CMI standard) [4] , [3] : Error correcting for the complementary base pairs to the last 12 base pairs in reverse order to identify samples from FASTQ from multiple samples
Per-sample FASTQ defaults (auto detect): Error detection for the FASTQ from 1 sample
Per-sample FASTQs; Phred offset: 33 [2] : Error detection for the FASTQ from 1 sample, uses Phred offset: 33 for measuring quality
Per-sample FASTQs; Phred offset: 64 [2] : Error detection for the FASTQ from 1 sample, uses Phred offset: 64 for measuring quality
For information regarding FASTQ formats please go to the FASTQ wikipedia page.
For more information regarding Demultiplexing please go to the Multiplexed wikipedia page.
Default Parameters Set
barcode type (required): Type of barcode used
max bad_run_length (required): Max number of consecutive low quality base calls allowed before truncating a read
max barcode_errors (required): Maximum number of errors in barcode
min per_read_length_fraction (required): Minimum number of consecutive high quality base calls to include a read
phred offset (required): Ascii (character that corresponds to a Phred score) offset to use when decoding phred scores
phred quality threshold (required): Minimum acceptable Phred quality score
rev comp (required): Reverse complement sequence before writing to output file
rev comp_barcode (required): Reverse complement barcode reads before lookup
rev comp_mapping_barcodes (required): Reverse complement barcode in mapping before lookup
sequence max_n (required): Maximum number of N characters allowed in a sequence to retain it
Deblurring¶
Note that sff data cannot be deblurred
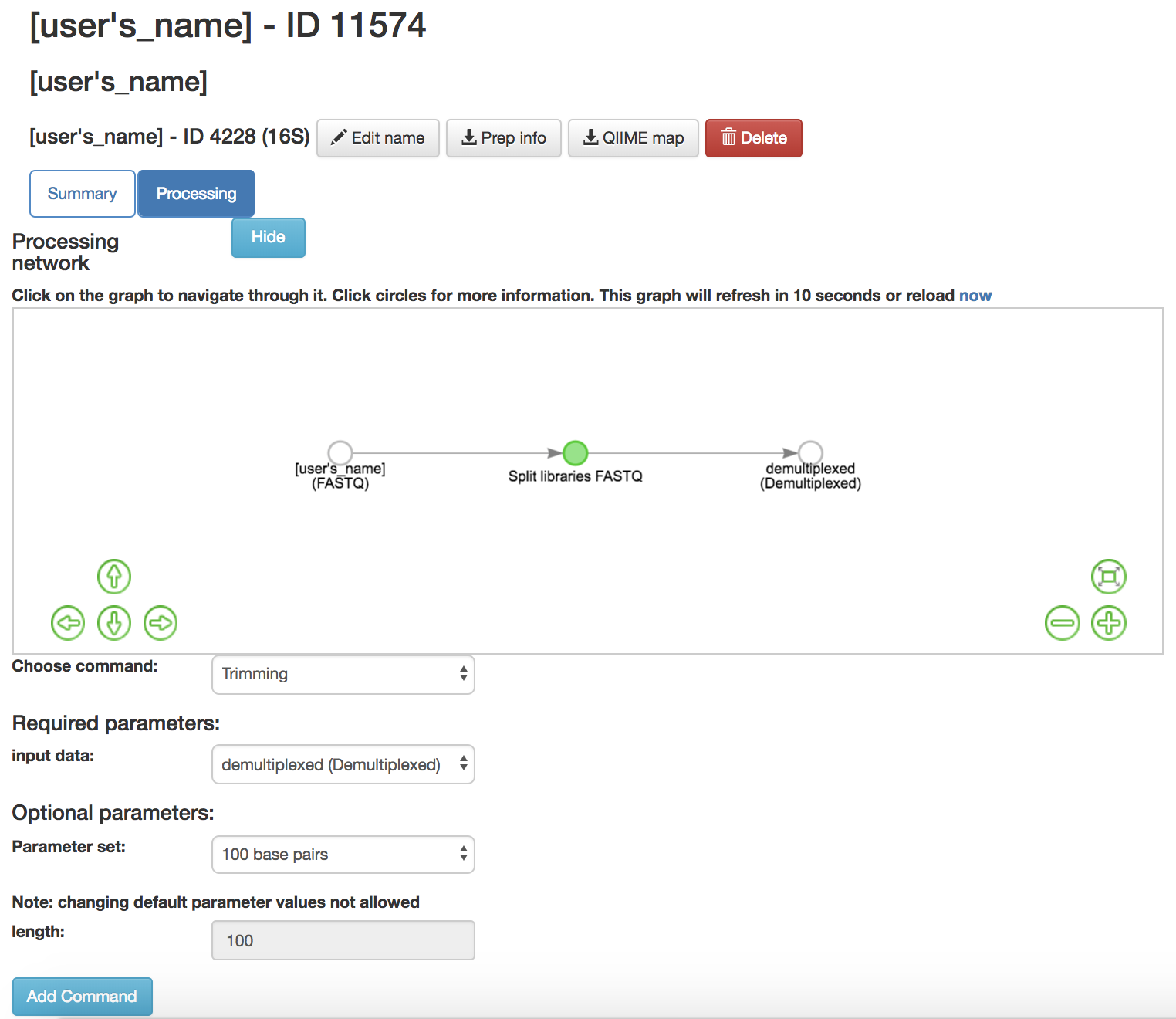
Trimming: Removes base pairs from the sequences
Input Data (required): Data being trimmed
Parameter Set (required): How many bases to trim off
90 base pairs- Keeps first 90 base pairs from the sequences
100 base pairs- Keeps first 100 base pairs from the sequences
125 base pairs- Keeps first 125 base pairs from the sequences
150 base pairs- Keeps first 150 base pairs from the sequences
200 base pairs- Keeps first 200 base pairs from the sequences
250 base pairs- Keeps first 250 base pairs from the sequences
300 base pairs- Keeps first 300 base pairs from the sequences
Command from Trimmed Artifact:
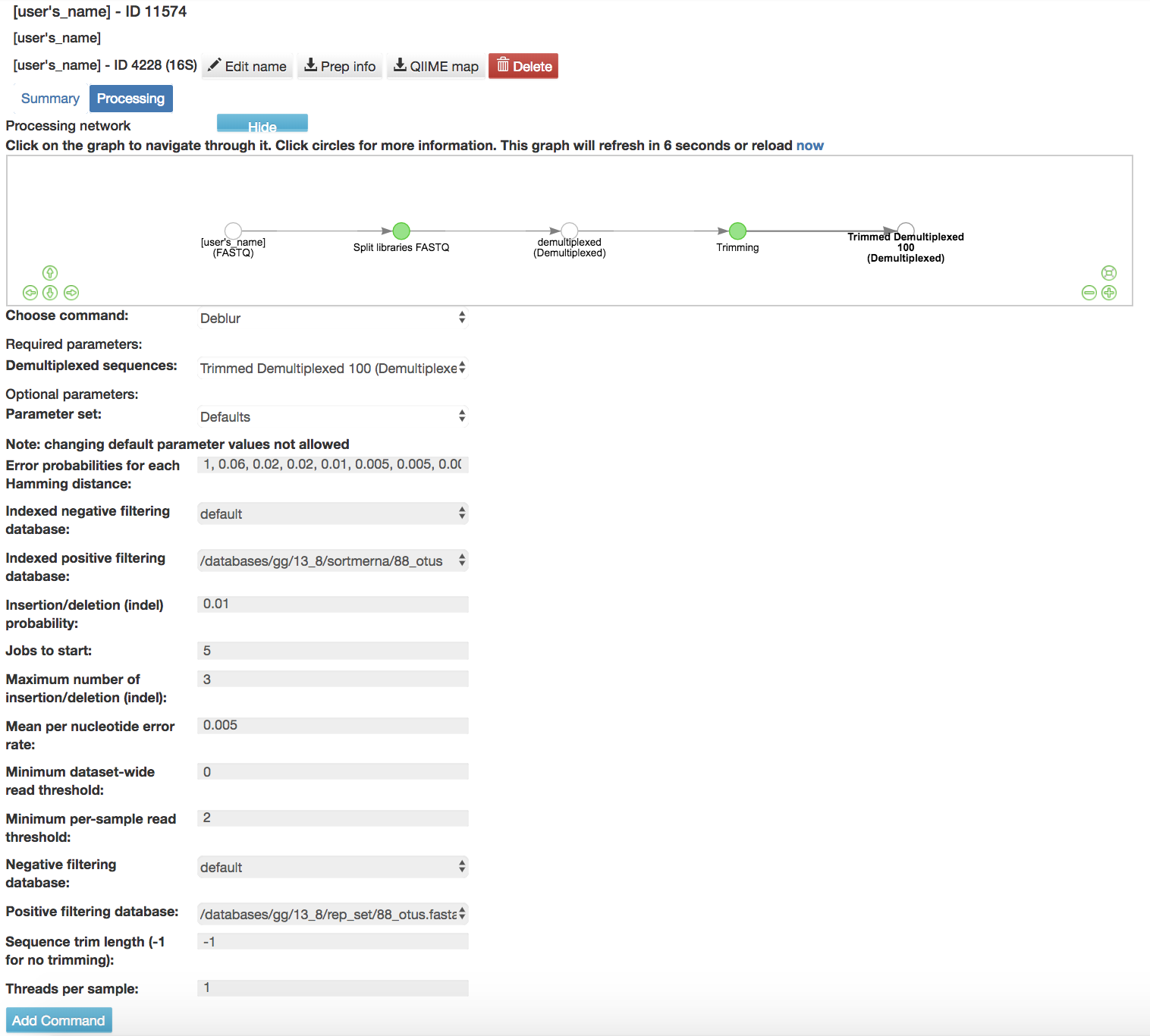
Deblur Workflow: Removes sequences due to error and does not take into account if sequences are found in a database
Default Parameters
Error probabilities for each Hamming distance (required): List of error probabilities for each hamming distance
Length of list determines number of hamming distances taken into account
Indexed negative filtering database (required): Indexed version of the negative filtering database
Indexed positive filtering database (required): Indexed version of the positive filtering database
Insertion/deletion (indel) probability (required): Insertion/deletion probability
Jobs to start (required): Number of workers to start (if to run in parallel)
Maximum number of insertion/deletion (indel) (required): Maximum number of allowed insertions/deletions
Mean per nucleotide error rate (required): Mean per nucleotide error rate
Used for original sequence estimate if the typical Illumina error wasn’t passed for the original
Minimum dataset-wide read threshold (required): Keep only the sequences which appear at this many times study wide (as opposed to per-sample)
Minimum per-sample read threshold (required): Keep only the sequences which appear at this many times per sample (as opposed to study wide)
Negative filtering database (required): Negative (artifacts) filtering database
Drops all sequences which align to any record in this
Positive filtering database (required): Positive reference filtering database
Keeps all sequences permissively aligning to any sequence
Sequence trim length (-1 for no trimming) (required): Sequence trim length
Threads per sample (required): Number of threads to use per sample
Deblur Reference Hit Table [5] : Only contains 16S deblurred sequences
To download the deblurred phylogenetic tree that can be imported into QIIME2 to be used in commands select insertion_table.relabelled.tre under “Available Files”
Deblur Final Table [5] : Contains all the sequences.
Closed-Reference OTU Picking¶
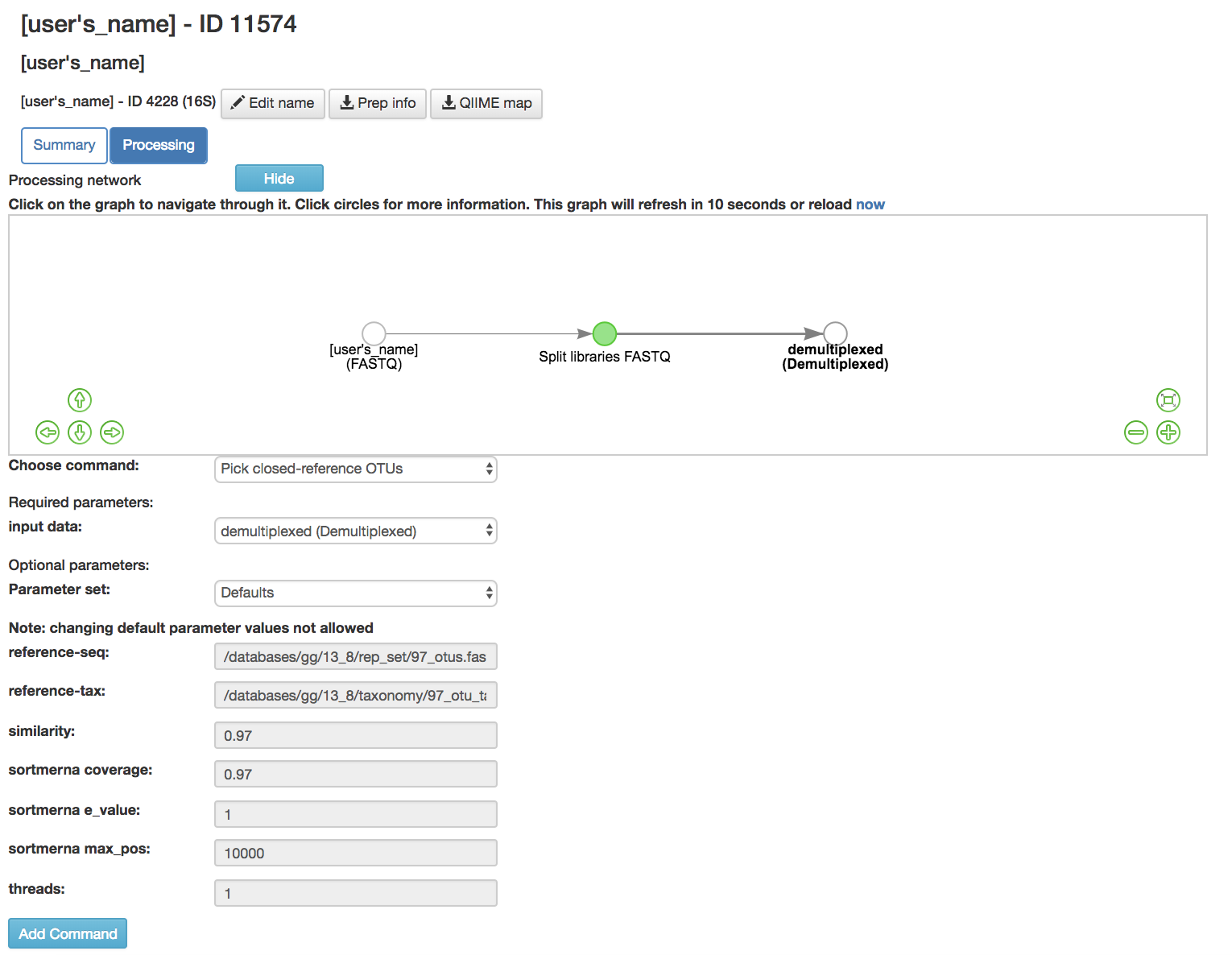
Pick Closed-Reference OTUs [6]: Removes sequences that do not match those found in a database
Input data (required): Data being close referenced
Parameter Set (required): Chooses the database to be compared to
Default Parameters (required)
Reference-seq (required): Path to blast database (Greengenes [7], Silva 119 [8] , UNITE 7) [9] ) as a fasta file
Reference-tax (required): Path to corresponding taxonomy file (Greengenes [7] , Silva 119 [8] , UNITE 7 [9] )
Similarity (required): Sequence similarity threshold
Sortmerna coverage [10] (required): Minimum percent query coverage (of an alignment) to consider a hit, expressed as a fraction between 0 and 1
Sortmerna e_value [10] (required): Maximum e-value when clustering (local sequence alignment tool for filtering, mapping, and OTU picking) can expect to see by chance when searching a database
Sortmerna max-pos [10] (required): Maximum number of positions per seed to store in the indexed database
Threads (required): Number of threads to use per job